Priorities in Cardio-Oncology Basic and Translational Science
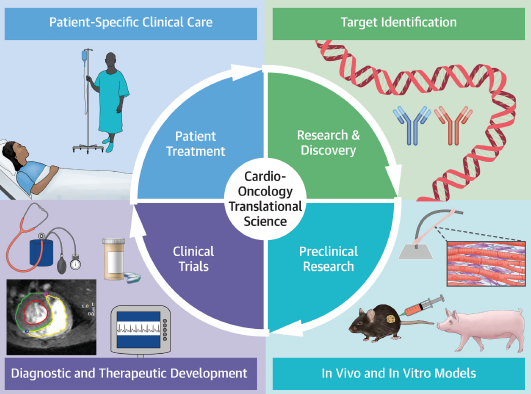
GCOS 2023 Symposium Proceedings: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review Despite improvements in cancer survival, cancer therapy–related cardiovascular toxicity has risen to become a prominent clinical challenge. This has led to the growth of the burgeoning field of cardio-oncology, which aims to advance the cardiovascular health of cancer patients and survivors, through actionable and translatable science. In […]
Remote Ischemic Conditioning for Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity The Need to Protect the Most Vulnerable

This article is authored by 2 PIs of RESILIENCE (María Gomes-Silva from IPO Lisbon & Borja Ibanez from CNIC Spain). This editorial summarizes the results of the 2 first trials testing remote ischemic conditioning in the context of anthracycline cardiotoxicity. In this article, the 2 trials are described and their results put into perspective of […]
Remote ischaemic conditioning: defining critical criteria for success—report from the 11th Hatter Cardiovascular Workshop
The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute biennial workshop, originally scheduled for April 2020 but postponed for 2 years due to the Covid pandemic, was organised to debate and discuss the future of Remote Ischaemic Conditioning (RIC). This evolved from the large multicentre CONDI-2–ERIC–PPCI outcome study which demonstrated no additional benefit when using RIC in the setting of […]
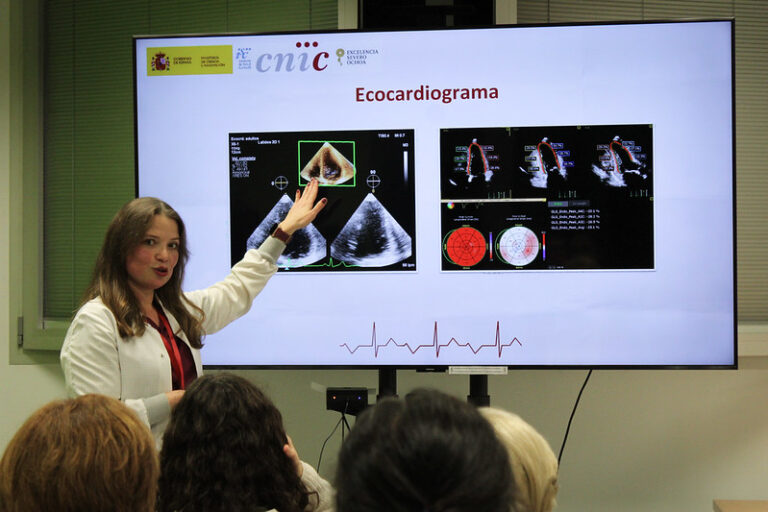
La búsqueda de un marcador precoz de cardiotoxicidad inducida por antraciclinas

There is a strong need to identify (bio)markers that can detect early stages of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC). In this editorial, 2 RESILIENCE researchers present the current state of the art of the field. They discuss data from al original paper published in the same issue of the journal by Bonny Ky´s team, showing that paraoxonase-1 […]
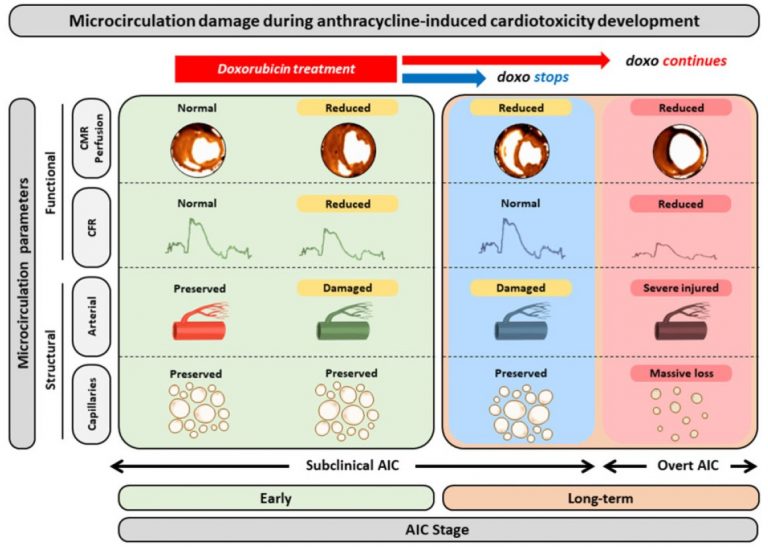
Daño de la microcirculación coronaria en la cardiotoxicidad por antraciclinas
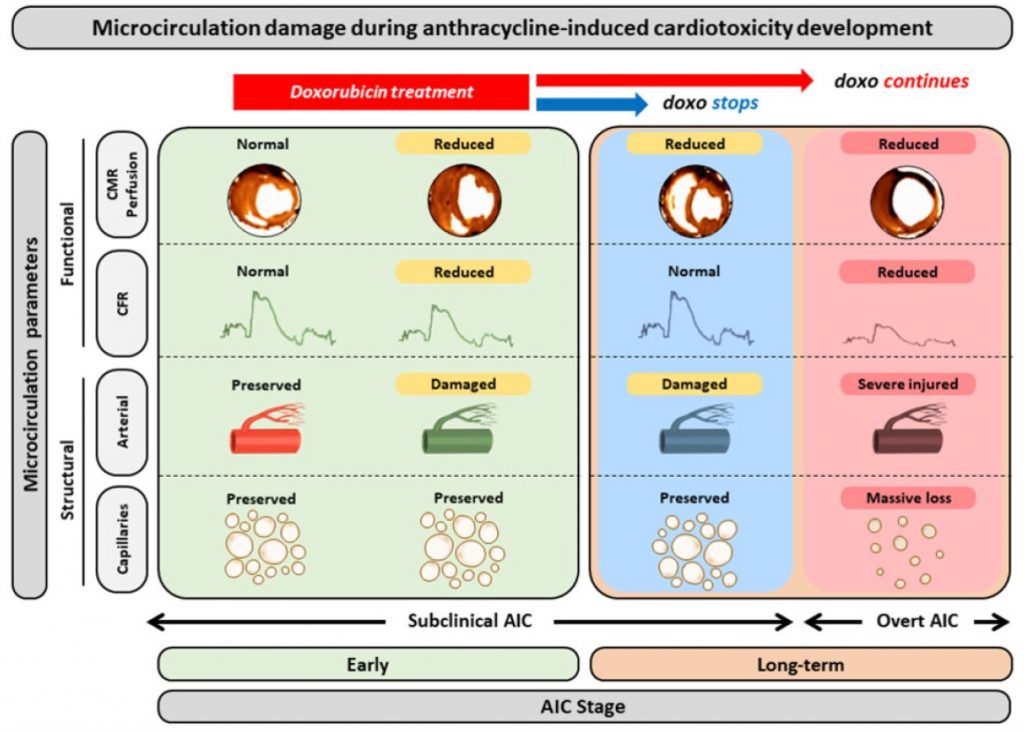
By using a highly translatable large-animal model, this work shows that cumulative exposure to anthracycline results in an irreversible damage to the heart microcirculation. The microcirculation injury is observed even before overt left ventricular cardiac systolic dysfunction (surrogate for overt cardiotoxicity) is present. Cardiac microcirculation damage is associated with poor clinical outcome in general, and […]
El precondicionamiento isquémico remoto mejora la cardiotoxicidad inducida por antraciclinas y mantiene la integridad mitocondrial.

Serial cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) evaluation of a highly translatable large-animal (pig) model of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC) shows that cumulative exposure to anthracyclines results in significantly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction and extensive mitochondrial fragmentation. Remote Ischemic Conditioning applied before each anthracycline cycle preserved cardiac contractility and left ventricular ejection fraction in long-term CMR exams. […]
Protección contra la cardiotoxicidad de la quimioterapia para el cáncer: ¿Un nuevo objetivo para el condicionamiento isquémico remoto?
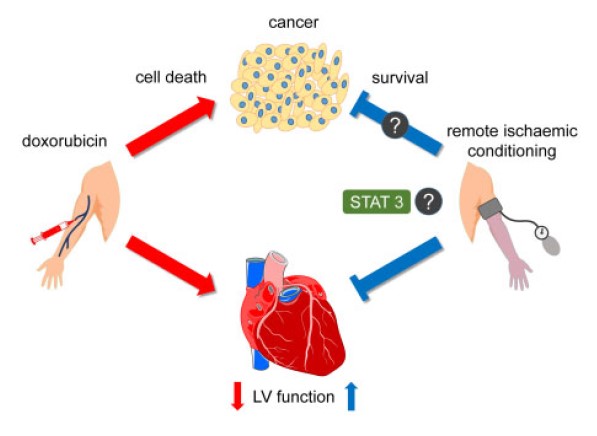
Editorial article highlighting the strong potential of remote ischemic conditioning to prevent anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. This intervention will be tested within RESILIENCE project.